What is BIM Software?
A beginner's guide
BIM software is a game-changer in the construction and built asset industry. It is a tool that has revolutionized how construction projects are managed. For beginners entering this field, understanding what BIM software is—and why it’s important—is a crucial first step.
This guide will walk you through the basics of BIM software, the benefits it offers, and how it’s shaping the future of built asset management.
What is BIM software?
BIM software, a common abbreviation for Building Information Modeling software, is a digital tool that helps professionals design, visualize, and manage buildings and built infrastructure. Unlike traditional CAD programs that only create 2D drawings or 3D models, BIM software integrates detailed information about every component of a building – including materials, quantities, timelines, and maintenance data.
With BIM software, the model becomes a centralized database that is accessible and editable by architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers. It goes beyond simple visual representation and supports collaborative decision-making throughout the construction project’s lifecycle.
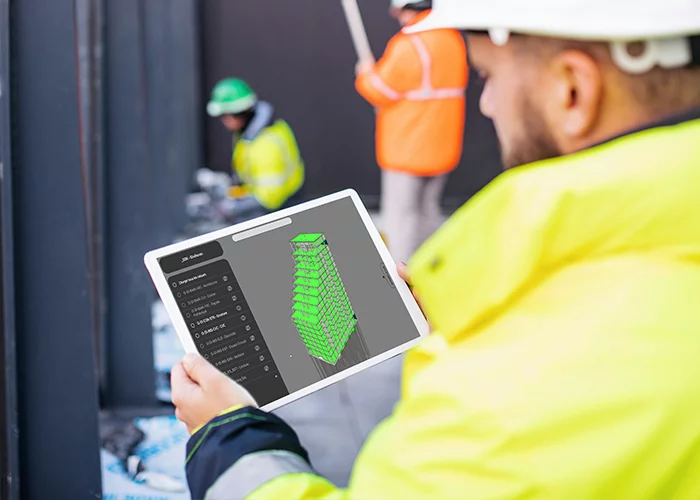


Main features of BIM software
How exactly does BIM software work? Understanding the features of BIM software helps highlight its value:
- 3D modeling: Create intelligent models that include both geometric and functional data.
- Data integration: Store information like cost estimates, schedules, and specifications within the model.
- Collaboration tool: Multiple teams can work on the same model in real-time, improving communication.
- Clash detection: Identify and resolve design conflicts before construction begins.
- Lifecycle management: BIM supports everything from the initial design to facility management, after project completion.
Benefits of using BIM software
The benefits of BIM software are far-reaching and impact every stage of a construction project, from early concept design to long-term operations. Here’s a deeper look into why building information modeling has transformed the industry:
1. Improved design accuracy
With BIM software, design errors and omissions are significantly reduced. Intelligent components within the model respond to changes dynamically—when one element is updated, all related components adjust accordingly. This ensures higher accuracy and consistency in drawings and documentation.
2. Enhanced collaboration
BIM software enables real-time collaboration between architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders. Cloud-based models allow teams to access the latest project version from anywhere, reducing miscommunication and redundant work. This offers an integrated approach and it helps avoid misunderstandings, avoiding costly delays.
3. Cost and time efficiency
By detecting design conflicts early and streamlining project planning, BIM helps reduce change orders, construction rework, and material waste. Accurate quantity takeoffs and scheduling allow for better budgeting and timeline adherence, translating into significant cost and time savings over the life of the project.
4. Clash detection and risk reduction
One of the standout benefits of BIM software is its clash detection capability. The software can automatically highlight conflicts—such as HVAC ducts intersecting with structural beams—before construction begins. This proactive problem-solving reduces the risk of on-site issues and enhances overall project safety.
5. Better visualization and communication
With BIM, stakeholders can visualize a project in 3D from its earliest stages. This helps clients and decision-makers understand design intent, explore options, and provide informed feedback. Virtual walkthroughs and photorealistic renders can also be generated to improve engagement.
6. Lifecycle asset management
BIM software supports the entire lifecycle of a building, not just the construction phase. Facility managers can use the model to track maintenance schedules, equipment data, warranties, and even perform renovations or retrofits with minimal disruption. The result is better asset performance and long-term cost control.
7. Sustainability and energy efficiency
By simulating energy performance, daylighting, and material use, BIM software allows architects and engineers to design more sustainable buildings. Optimizing energy efficiency early in the design process leads to lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact, supporting green building certifications like LEED or BREEAM.
8. Regulatory compliance
BIM software helps ensure compliance with building codes, safety regulations, and industry standards. Automated checks and model validation tools can flag violations before drawings are submitted for approval, reducing the risk of non-compliance and project delays.
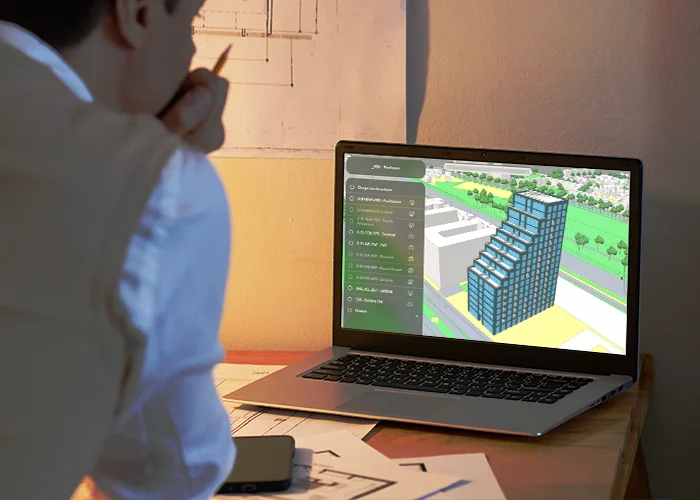

Applications of BIM software in construction
As we’ve already pointed out, the use of Building Information Modeling spans across the entire lifecycle of a built asset. But it is also used across various sectors of the built asset industry:
- Architecture: Conceptual design, spatial planning, and visual presentations.
- Structural engineering: Load analysis, structural integrity checks, and steel detailing.
- MEP engineering: Layouts and coordination of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems.
- Construction: Scheduling, cost estimation and logistics planning.
- Facility management: Post-construction operations, maintenance scheduling, and space management.
The future of BIM Software
As the built asset industry embraces digital transformation, BIM software is evolving rapidly through:
- AI and Automation: Intelligent suggestions for design optimization and risk detection.
- Cloud-Based BIM: Seamless collaboration from anywhere, on any device.
- AR/VR Integration: Immersive visualization for clients and stakeholders.
- Sustainable Design: Enhanced analysis tools for energy efficiency and carbon impact.
- Digital Twins: BIM is a critical input to a digital twin and will likely evolve together with it. Digital twins use BIM data as a starting point, then extend and evolve it with real-time operational data from sensors, IoT devices, and maintenance records once the building is in use.
BIM is also a key enabler of smart cities and digital twins, helping cities plan and manage infrastructure more effectively.
BIM software is more than just a design tool—it’s a comprehensive solution for planning, executing, and managing construction projects. By embracing building information modeling, professionals can unlock greater efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability in their work. Whether you’re an architect, engineer, or project manager BIM software is an investment that will pay off.
Virtual Design & Construction Management with Thinkproject
Thinkproject’s Virtual Design & Construction (VDC) solutions streamline project management through improved collaboration and error-free designs. With BIM collaboration, which is included in VDC, we focus on design coordination and model assurance, offering model issue management and visualisation.But VDC goes beyond traditional BIM software, providing a comprehensive approach to managing construction projects, through:
- Integrating several project aspects: scheduling and 4d simulation, cost management (5D), collaboration workflows.
- Stakeholder involvement and collaboration: VDC emphasizes integrated processes and early collaboration, reducing redundant work and improving decision-making early in design.
- A focus on impact and results: Going beyond simply creating a rich 3D model, VDC aims to improve project performance, collaboration, and construction quality.